You are given a node that is the beginning of a linked list. This list always contains a tail and a loop. Your objective is to determine the length of the loop.
For example in the following picture the tail's size is 3 and the loop size is 12:
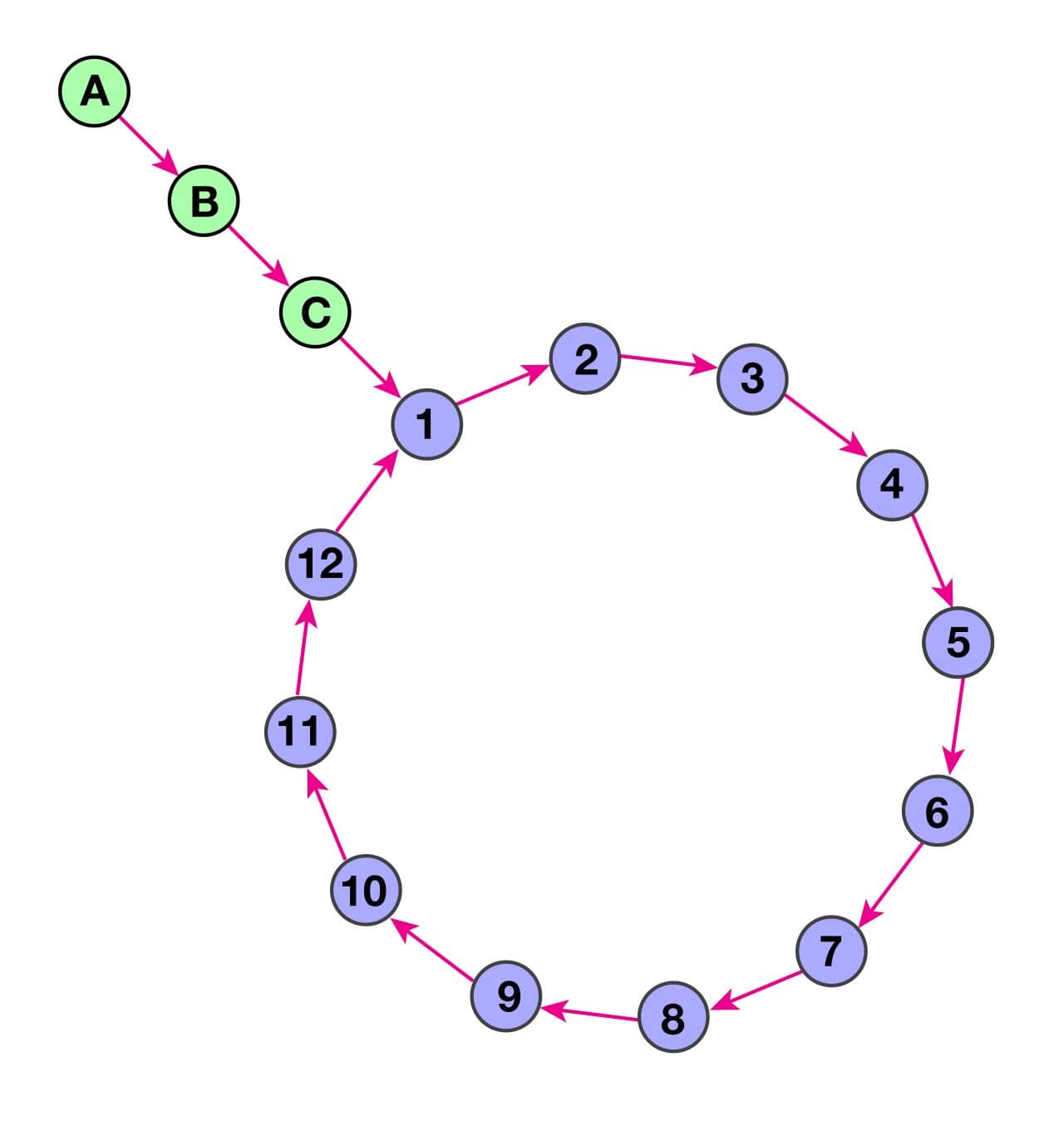
| // Use the `getNext()` method to get the following node. nodePtr->getNext() |
Solution
#include <map>
int getLoopSize(Node* startNode) {
Node *next, start;
int result = 0;
std::map<Node*, int> table;
next = startNode->getNext();
table[next]++;
while (next != NULL) {
next = next->getNext();
if (table[next] == 1) {
break;
}
table[next]++;
}
while (next != NULL) {
next = next->getNext();
if (table[next] == 2) {
break;
}
table[next]++;
result++;
}
return result;
}
IcyMan의 코드
int getLoopSize(Node* startNode) {
Node* turtle = startNode;
Node* rabbit = startNode->getNext();
while (turtle != rabbit) {
turtle = turtle->getNext();
rabbit = rabbit->getNext()->getNext();
}
turtle = turtle->getNext();
int count = 1;
while (turtle != rabbit) {
turtle = turtle->getNext();
count++;
}
return count;
}
Daniyal Qadri의 코드
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <type_traits>
#include <vector>
int getLoopSize(Node *startNode) {
std::vector<Node *> addrs;
while (std::find(addrs.begin(), addrs.end(), startNode) == addrs.end()) {
addrs.push_back(startNode);
startNode = startNode->getNext();
}
return addrs.size() -
std::distance(addrs.begin(),
std::find(addrs.begin(), addrs.end(), startNode));
}
후기
루프는 몇 개의 노드로 이루어져 있는지 찾아내는 문제였다. 나는 두 개의 반복문을 사용하였고, 문제를 해결했음에도 이 것밖에 안되는지 좌절했다. 하지만 첫 번째 남의 코드를 보고서는 아, 보통 반복문을 두 번 사용해야 풀 수 있구나를 깨달으며 안도의 한숨을 내쉬었다. 하지만 그도 잠시, 두 번째 남의 코드를 보고서는 아 STL의 세계는 참 넓었지! 를 깨달으며 다시 한번 공부의 의지를 불태웠다. 후훗. 하늘 위에 하늘이 있다는 말 누가 했는지 참 잘 만든 말인 거 같다.
(url: https://www.codewars.com/kata/52a89c2ea8ddc5547a000863)
728x90
'연습장' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Sequences and Series (0) | 2021.11.04 |
|---|---|
| My smallest code interpreter (aka Brainf**k) (0) | 2021.11.04 |
| Human Readable Time (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| Product of consecutive Fib numbers (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| Greed is Good (0) | 2021.10.27 |